ATM Backhaul .
The "pipe" between your local exchange and where it becomes part of the ATM Cloud.
A common pipe has a capacity of 155Mb, although larger exchanges may have multiple or larger 622Mb pipes.
Some small
exchanges may be subtended /"piggy backed" to a larger exchange in a nearby town, and as such will have a lesser capacity
of 30Mb.
It is assumed that these pipes are segmented with various amounts of bandwidth as allocated by the Virtual Path.
ATM Cloud (MSiP).
BT's ATM network between various points, which can take many different paths/routes.
It carries traffic in pure ATM
form and is called the Multi-Service intranet Platform (MSiP). Since it is impossible to know exactly which route traffic
will traverse, an ATM network is depicted as a cloud.
BT's ATM network was originally built in the 1990's to handle traffic for business customers who required such services
as intranets on leased lines. Today it also carries IP packets as an ATM stream for internet customers to and from the Colossus
backbone.
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) is a networking technology based on transferring data in cells or packets of a fixed size
over a dedicated connection.
The cell used with ATM is relatively small compared to units used with older technologies.
The small, constant cell size allows ATM equipment to transmit video, audio, and computer data over the same network, and
assure that no single type of data hogs the line.
In the UK BT uses the networking protocol PPPoA (Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM) over this part of the network for the
transmission of data packets.
As a side note some other countries (such as the US) use PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) for adsl.
PoP (Point of Presence).
Location or point where a network can be accessed. - See also Colocation Center.
RAS / B-RAS (Broadband Remote Access Server).
Although the RAS could be thought of as a "super exchange" for adsl, in actual fact it is hardware that is located in strategic
points throughout the UK. In general networking terms the RAS would be known as a L2TP Access Concentrator (LAC).
The RAS is the first major hop of your connection, and it is here that the login authentication to your ISP is carried
out, and you are allocated your IP address.
It is also at this point that you use the bt_tests such as bt_test_user@startup_domain
to bypass your ISP and route you directly to the bt.net intranet.
There are currently 11 RAS's that serve all the various local exchanges:-
Birmingham, Bletchley, Ealing, Edinburgh, Ilford, Kingston, Manchester, Reading, Sheffield, Milton Keynes, Faraday.
Due to the way BTw perform their routing, you may find that the RAS that you connect via is not necessarily the nearest
to you location wise - its quite common for different DSALMs at your exchange to be routed to several different RAS's.
Anyone whose ISP uses a BT Central Plus product should be able to see the RAS as their "first hop". Some ISPs however purchase
their own central pipes from BT and as such this hop in the routing is hidden. Users with ISPs who have their own centrals
may be able to find out which RAS they are connected to by following the instructions here.
Authentication.
Authentication of your adsl connection is carried out at the RAS.
A very simplified explanation would be to say that
a BT RADIUS server at the RAS would establish an L2TP connection to the ISP's RADIUS server.
The BT RADIUS server authenticates the domain part of the username and from this determines the ISP's Central and associated
router. The ISP's RADIUS then authenticates the enduser by their username and password. Once both of these have been verified
an IP address is assigned to the user. The whole authentication process is actually a lot more complicated, and a more in-depth
view can be seen here.
RADIUS default timers:- Home gateway router timeout = 10, no of retries =2.
SSB (Service Selection Barring) is implemented at the RAS during the authentication process.
It is
SSB that stops users from being able to access two different ISPs at the same time, and BT Wholesale set up your connection
so that it can only connect to your particular ISP's realm.
When you migrate, BTw will change the SSB details, by removing your old ISP details and inputting your new ISP information
so that you can only connect to the new ISP.
Colossus IP Network.
BT's main Internet Backbone built in the late 1990's to carry IP traffic. It consists of a massive network of fibres and
powerful (gigabit) routers which can operate at over a billion bits per second. Every day it carries many gagbits of internet
traffic around the UK and linking to international internet backbones. (Central Plus ISPs only).
Home Gateway.
The tunnel endpoints on which PPP sessions from the Colossus Network are terminated and where it joins the ISP Central
Pipes is known as a home gateway.
The Home Gateway is a cluster of LTS's (L2TP Tunnel Switches). The amount of switches required depends upon the size and
type of Central Pipe used by the ISP - for example a 155 Mbps Central terminates on 2 LTS' whilst a 622 Mbps pipe will terminate
on 12 LTS'.
The test login bt_test_user@ispdomain.com is carried out at this level.
BT Central Pipe.
A BT Central connection provides the link between the ISP's network and the BT network.
An IPStream ISP who manages
their own network traffic will lease one or more Central Pipes from BT, most commonly being multiples of 155 Mbps or 622 Mbps.
If an ISP uses 622 Mbps pipes, they have an option of activating these in 155Mbps segments.
A 622Mb central is actually 2 x Gigabit Ethernet Fibre Optic cables (1000 BaseSX) that terminate on 12 tunnel endpoints
(Home gateways/LTS's).
The 622Mbps design uses a total of 12 LTS's and provides 46.3Mbps (of end user IP traffic) per LTS.
A 622Mb central pipe can hold up to a maximum of 25,600 simultaneous sessions, and can sustain up to 622 Mbit/s of downstream
traffic plus up to 311 Mbit/s upstream throughput.
However it should be noted that because its presented as IP over PPP
over L2TP over UDP over IP over Ethernet typical EU downstream throughput will be 557Mit/s.
There more indepth information on BT Centrals Page.
All ISPs run their Networks slightly differently as the amount of capacity and requirements will vary depending upon their
type of users.
BT Wholesale offer a service called Central Plus whereby BTw do the majority of the routing for ISPs and takes customers
of these ISP's adsl traffic straight out to the Internet. Customers of ISPs that use Central Plus will see BT routing before
their ISP details when they do a tracert.
Larger ISPs tend to lease Central Pipes from BT, so that they can route and manage users traffic themselves.
Below is a diagram of Plusnet's network. The diagram is interactive - move your mouse over various points to identify the
equipment and a link to more information about the equipment.
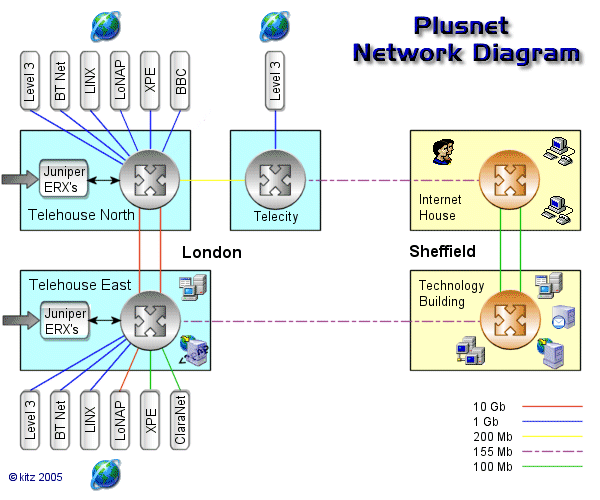
Central Pipes.
Generic Information on BT Central Pipes can be found on my page How adsl works 2.
Current information on Plusnet's Central Pipes in use can be found on its own page here.
Edge Routers.
|
These powerful routers terminate the ISP end of the Central and control the traffic flow in and out of the internet.
Plusnet currently have 5 Juniper ERX 1440's and are the first hop you will see when performing a tracert.
These Junipers act as the aggregation point where service providers accept and authenticate connections for tens of thousands
of customers. The E-series allows authenticated users access only to the bandwidth, QoS, services and features that they have
subscribed to. Therefore, it is the key place in the network to control, deliver and account for customer services.
Each 14-slot Router contains a 40Gbps switch fabric and supports full redundancy. 12 slots are dedicated to line modules.
A 155Mb line card on a Juniper can sustain 8000 subscribers up to a maximum of 48,000 therefore a Juniper could take traffic
from more than a single 622 Mb pipe. |

Full size images:
Front Rear PDF
More info at juniper.net
|
Gateway routers.
|
An ISP will have a multitude of gateway and internal routers whose task it is to direct traffic on to the next part of
our journey.
Depending upon where you have requested data from, these routers will pass you on to the best path to ensure that your
data gets to its destination. |
 |
Transit Providers
|
These are companies that specialise in forwarding data between various countries and overseas. An ISP may use several different
transit providers for different routing. The ISP will have to pay the organisation transit costs for data sent and received.
Well known transit providers include Level 3, BT net, Cogent, Sprint. |
|
Colocation Center
|
A colocation center (or colo) is a large data center where ISPs and other telecommunication companies site their networking
equipment on secure premises.
These premises provide air conditioned rooms which are vital for powerful servers and routers. They offer high standards
of security against disasters such as fire, intrusion, and power outages.
Telehouse (North and East London) and Telecity (London and Manchester) are 2 organisations in the UK which offer colo facilities. |

Telecity London
|
Peering Points.
|
Peering Points offer ISPs a point where they can exchange traffic with each other. Peering is offered by organisations
located in a colocation center.
The idea of peering is that ISPs can reduce their transit costs on the internet backbone. It also has an added benefit
that it can provide a more direct access point to another ISP.
LoNAP, LINX, XchangePoint (XPE) and MaNAP are some of the companies in the UK that offer peering services. |
|
Servers.
Powerful computers that are dedicated to a specific task. An ISP will have many different types of Servers. The server
will host a specific type of information and then "serve" the data to the user. Some essential Servers are Mail, Web, File
and database, other types of servers that an ISP may have are dedicated games servers, CGI servers, SQL etc.
|
|
|
|
ftp, web stats and mail servers. |
NetApp Storage Cluster |
|
|

